Editor-In-Chief:C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D.[1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Mohamed Moubarak, M.D.[2]
Possible causes of Pulsus bigeminus (Medical Symptom)Pulsus bigeminus is a cardiovascular phenomenon characterized by groups of two heartbeats close together. Pulsus bigeminus is differentiated from the pulsus dicroticus by the fact that in the latter there is only one contraction of the heart for every two beats of the pulse, while in pulsus bigeminus there are two contractions of the heart, which follow one another rapidly and are separated from the preceding and succeeding contractions by a longer pause.
May 04, 2017 After each heartbeat is a pause, and then a predictable heartbeat, and then a pause, and so on. But if you have a condition known as bigeminy, each normal heartbeat is followed by a beat that.

- Pulsus bigeminus is a cardiovascular phenomenon characterized by groups of two heartbeats close together followed by a longer pause.
- Pulsus bigeminus (195103000); Bigeminal pulse (195103000) Recent clinical studies. Extensive subcutaneous emphysema and hypercapnia during laparoscopic.
Overview
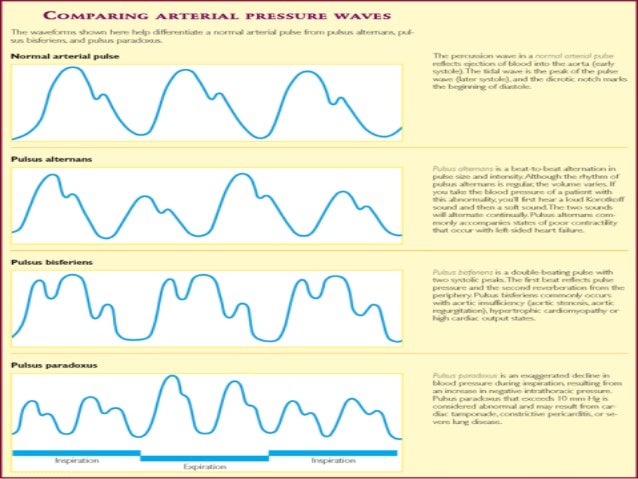
Pulsus bigeminus is a cardiovascular phenomenon, in which two heartbeats occur close to each other followed by a long pause. The second pulse is weaker than the first, and it is caused by premature contractions after every other beat, usually of the ventricles.
Causes
Overview
Pulsus bigeminus may be innocent and a temporary phenomenon, but mostly seen in cases of hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy.
Life Threatening Causes
Life-threatening causes include conditions which may result in death or permanent disability within 24 hours if left untreated. Pulsus bigeminus in itself is not a life threatening condition.
Common Causes
The most common cause of pulsus bigeminus is hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy, other causes include:
Causes by Organ System
| Cardiovascular | Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy, myocardial infarction |
| Chemical / poisoning | No underlying causes |
| Dermatologic | No underlying causes |
| Drug and Toxin Side Effect | Beta blocker, calcium channel blocker, digoxin |
| Ear Nose Throat | No underlying causes |
| Endocrine | Hypothyroidism |
| Environmental | No underlying causes |
| Gastroenterologic | No underlying causes |
| Genetic | [No underlying causes |
| Hematologic | No underlying causes |
| Iatrogenic | No underlying cause |
| Infectious Disease | No underlying causes |
| Musculoskeletal / Ortho | No underlying causes |
| Neurologic | No underlying cause |
| Nutritional / Metabolic | No underlying cause |
| Obstetric/Gynecologic | No underlying cause |
| Oncologic | No underlying causes |
| Opthalmologic | No underlying causes |
| Overdose / Toxicity | [No underlying causes |
| Psychiatric | No underlying causes |
| Pulmonary | No underlying causes |
| Renal / Electrolyte | Hyperkalemia |
| Rheum / Immune / Allergy | No underlying causes |
| Sexual | No underlying causes |
| Trauma | No underlying causes |
| Urologic | No underlying causes |
| Miscellaneous | No underlying causes |
Causes in Alphabetical Order
References

Template:WikiDoc Sources
Pulsus Bigeminus Pathophysiology
